Real account 10
There is no hard and fast rule that all assets should be tangible. Elements effected by the transaction are
Free forex bonuses
Account types or kinds of accounts - personal, real, nominal
Personal accounts
Tangible
In the initial stages of learning accounting, we assume real accounts to be those representing tangible elements. This is because all the elements that we deal with at this stage have that characteristic.
There is no hard and fast rule that all assets should be tangible.
Eg : goodwill of an organisation is an intangible asset.
There are many other ways the terms real accounts and the term asset can be interpreted and understood. For now, please, stick to the simple understanding that assets are tangible aspects and are thus identified as real accounts.
Nominal accounts
We do not come across such accounts till a later stage of our learning. For now, please, assume that such accounts exist.
Profit on sale of asset a/c - representing the profit made on sale of assets, a gain.
We do not come across such accounts till a later stage of our learning. For now, please, assume that such accounts exist.
Every account head belongs to one of the three types
We use this property to identify the nature of an account sometimes. Where an account cannot be classified under two types, it should be the third type.
- Nominal accounts are accounts other than personal and real accounts
- Real accounts are accounts other than personal and nominal accounts
- Personal accounts are accounts other than real and nominal accounts
Accounting system - minimum accounting heads
Where the information needed by the organisation is very minimal, it can account for the transactions relating to its business with a minimum of four accounting heads.
Assets and liabilities
Assets a/c
All the real accounts and the personal accounts representing debtors are to be assumed to be represented by the account head named asset a/c. Asset a/c would take the place of furniture a/c, machinery a/c, land a/c, buildings a/c, shyam's a/c (debtor), bank a/c, cash a/c etc.
Liabilities a/c
Liabilities are generally made up of personal accounts representing owned capital and loaned capital. Liabilities a/c would take the place of capital a/c, ram's a/c (creditor) etc.
Note : assets and liabilities include only accounts of the type real and personal.
Incomes/gains and expenses/losses
Expenses/losses a/c
All the nominal accounts representing expenses and losses are to be assumed to be represented by the account head named expenses/losses a/c
Incomes/gains a/c
All the nominal accounts representing incomes and gains are to be assumed to be represented by the account head named incomes/gains a/c
Minimum five account heads
Thus to have a clear and better understanding/information regarding liabilities, the liabilities a/c is replaced by two accounts: capital a/c and liabilities a/c.
The more the information we need the more the accounting heads we have to maintain.
Therefore, the minimum accounting heads to be maintained would be 5 i.E. Capital a/c, liabilities a/c, assets a/c, expenses/losses a/c, incomes/gains a/c.
Elements effected by a transaction - identifying account type
The business is proposed to be started.
Started business with a capital of 1,00,000.
Since capital in the form of cash is being brought into the business, capital increases by 1,00,000 and cash increases by 1,00,000
Elements effected by the transaction are
Bought furniture for cash 25,000
Since furniture is being bought by paying cash, the value of furniture increases by 25,000 and the cash available with the business would reduce by 25,000.
Elements effected by the transaction are
Bought goods for cash 25,000 from M/s roxy brothers.
Since goods are bought by paying cash, the value of goods increases by 25,000 and the cash available with the business would reduce by 25,000.
Elements effected by the transaction are
Bought goods from mr. Shyam rao on credit for 10,000.
Since goods are bought on credit, the value of goods increases by 10,000. The liabilities of the business would increase by 10,000. This liability is indicated by an element identified by the name of the vendor who gave the goods on credit i.E. Mr. Shyam rao.
Elements effected by the transaction are
Sold goods for cash 20,000 to mr. Peter.
Since goods are sold by taking cash, the value of goods decrease by 20,000 and the cash available with the business would increase by 20,000.
Elements effected by the transaction are
Sold goods on credit to M/s bharat & co., for 10,000.
Since goods are sold on credit, the value of goods decreases by 10,000. A new asset in the form of a debtor (those who owe us) is created. The new asset is indicated by an element identified by the name of the organisation which purchased the goods on credit i.E. M/s bharat & co.
Elements effected by the transaction are
Paid cash into bank 60,000.
Since cash is paid into bank, the available cash reduces by 60,000. The amount paid into the bank is held by the bank on our behalf. The bank has to pay us the same whenever we ask for it. The bank therefore stands in the position of a debtor to us (those who owe us money). The amount of balance in the bank which is newly created increases from zero by 60,000.
Elements effected by the transaction are
Paid cash to mr. Shyam rao, 5,000
Since cash is paid to mr. Shyam rao, the available cash reduces by 5,000 and the liability in the name of mr. Shyam rao (the amount due to him) also reduces by 5,000.
Elements effected by the transaction are
Received cash from M/s bharat & co., on account, 8,000
Since cash is received from M/s bharat & co., the available cash increases by 8,000 and the asset (debtor) in the name of M/s. Bharat & co (the amount receivable from them) also reduces by 8,000.
What is a real account?
Definition: A real account is a permanent account in the general journal that does not close at the end of a period. In other words, these accounts stay open allowing their balances to accumulate and carry over to the next period for the company’s lifetime.
What does real account mean?
What is the definition of real account? Real accounts reflect the current and ongoing financial status of a company because they carry their balance forward into the next accounting period. These accounts are typically reported on the balance sheet at the end of the year as assets, liabilities, or equity.
These account balances change throughout the accounting period. Management can review the extent of these changes by comparing initial and final balance of each account. The final balance will become reported on the balance sheet at the end of the period and will be carried over to the next period becoming the initial balance for the next accounting period.
The relationship between real and nominal accounts is that a change in one of them might derive in a change on the other. This means that if a nominal account increases or decreases it will increase or decrease a permanent account.
Let’s illustrate this concept with an example.
Example
Young motors co. Is a startup company that produces motorcycles. Today is the first day of the company and its owners contribute the following things:
- Cash: $30,000
- Inventory: $25,000
- Fixed assets: $50,000
The company has no liabilities. After a few months of operations, the company has the following:
- Revenues: $25,000
- Cost of goods sold: $10,000
- Rent: $5,000
- Other expenses: $1,500
The accounting period started on january 1 and it will end on december 31.
At the end of the period, the revenues, cost of goods sold, rent, and other expenses are reported on the income statement as an $8,500 net income. These accounts are then closed with year-end closing entries to the retained earnings account leaving the company with the following permanent accounts that will carry over into the next period:
- Cash: $50,000
- Inventory: $15,000
- Fixed assets: $50,000
- Retained earnings: $115,000
Summary definition
Define real accounts: real account means a general journal account that isn’t closed at the end of the year.
Enable the (hidden) administrator account on windows 7, 8, or 10

Many people familiar with prior versions of windows are curious what happened to the built-in administrator account that was always created by default. Does this account still exist, and how can you access it?
The account is created in windows 10, 8, 7, or vista, but since it’s not enabled you can’t use it. If you are troubleshooting something that needs to run as administrator, you can enable it with a simple command.
Warning: the built-in administrator account has a lot more privileges than a regular administrator account—privileges that can easily get you into trouble if you use it regularly. We recommend only enabling the built-in administrator account if you are certain you need it to troubleshoot a specific problem and then disabling it when you are done. If you’re unsure whether you need it, you probably shouldn’t use it at all.
Enable built-in administrator account in windows
First you’ll need to open a command prompt in administrator mode by right-clicking and choosing “run as administrator” (or use the ctrl+shift+enter shortcut from the search box).
Note that this works the same in all versions of windows. Just search for cmd and then right-click on the command prompt icon in the start menu or start screen.
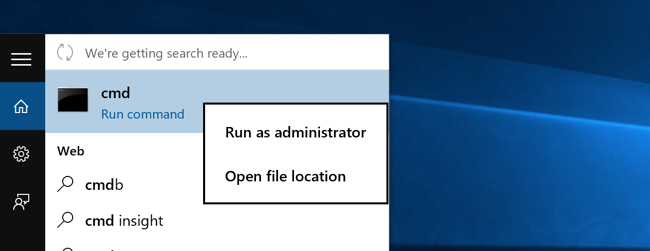
If you are in windows 8.X or 10 you can right-click on the start button and choose to open a command prompt that way.

Now type the following command:
Net user administrator /active:yes

You should see a message that the command completed successfully. Log out, and you’ll now see the administrator account as a choice. (note that this screenshot is from vista, but this works on windows 7 and windows 8 and windows 10)
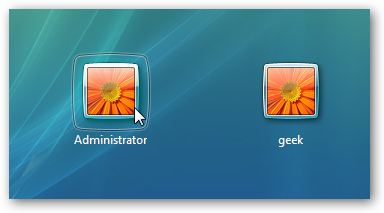
You’ll note that there’s no password for this account, so if you want to leave it enabled you should change the password.
Disable built-in administrator account
Make sure you are logged on as your regular user account, and then open an administrator mode command prompt as above. Type the following command:
Net user administrator /active:no

The administrator account will now be disabled, and shouldn’t show up on the login screen anymore.

Lowell heddings
lowell is the founder and CEO of how-to geek. He’s been running the show since creating the site back in 2006. Over the last decade, lowell has personally written more than 1000 articles which have been viewed by over 250 million people. Prior to starting how-to geek, lowell spent 15 years working in IT doing consulting, cybersecurity, database management, and programming work.
Read full bio »
Real account 10
As an existing XM real account holder you can simply register an additional account through the members area with 1 click. No additional validation is required.
Unlimited loyalty program
Earn XM points on every trade, then redeem those points for real cash rewards and trading bonuses.
Extra bonuses
Get additional exclusive bonuses throughout the year either on a seasonal basis or by invitation only.
Legal: this website is operated by XM global limited with registered address at no. 5 cork street, belize city, belize, CA.
Trading point holdings ltd is the holding company of trading point of financial instruments limited, XM global limited, trading point of financial instruments UK limited, trading point of financial instruments pty ltd, and trading point MENA limited.
Trading point of financial instruments limited is authorised and regulated by the cyprus securities and exchange commission (cysec) (licence number 120/10).
XM global limited is authorised and regulated by the international financial services commission (IFSC) (license number 000261/106).
Trading point of financial instruments UK limited is authorised and regulated by the financial conduct authority (FRN: 705428).
Trading point of financial instruments pty ltd is authorised and regulated by the australian securities and investment commission (AFSL 443670).
Trading point MENA limited is authorised and regulated by the dubai financial services authority (DFSA) (reference no. F003484).
Risk warning: forex and CFD trading involves a significant risk to your invested capital. Please read and ensure you fully understand our risk disclosure.
Restricted regions: XM global limited does not provide services for the residents of certain countries, such as the united states of america, canada, israel and the islamic republic of iran.
This website uses cookies
By clicking “continue”, you agree to the default cookie settings on our website.
XM uses cookies to ensure that we provide you with the best experience while visiting our website. Some of the cookies are needed to provide essential features, such as login sessions, and cannot be disabled. Other cookies help us improve our website’s performance and your experience through personalising content, providing social media features and analysing our traffic. Such cookies may also include third-party cookies, which might track your use of our website. You may change your cookie settings at any time.
For more information please read our cookie policy.
This website uses cookies
By clicking “continue”, you agree to the default cookie settings on our website.
XM uses cookies to ensure that we provide you with the best experience while visiting our website. Some of the cookies are needed to provide essential features, such as login sessions, and cannot be disabled. Other cookies help us improve our website’s performance and your experience through personalising content, providing social media features and analysing our traffic. Such cookies may also include third-party cookies, which might track your use of our website. You may change your cookie settings at any time.
Read more, or change your cookie settings.
Your cookie settings
What are cookies?
Cookies are small data files. When you visit a website, the website sends the cookie to your computer. Your computer stores it in a file located inside your web browser.
Cookies do not transfer viruses or malware to your computer. Because the data in a cookie does not change when it travels back and forth, it has no way to affect how your computer runs, but they act more like logs (i.E. They record user activity and remember stateful information) and they get updated every time you visit a website.
We may obtain information about you by accessing cookies, sent by our website. Different types of cookies keep track of different activities. For example, session cookies are used only when a person is actively navigating a website. Once you leave the website, the session cookie disappears.
Why are cookies useful?
We use functional cookies to analyse how visitors use our website, as well as track and improve our website’s performance and function. This allows us to provide a high-quality customer experience by quickly identifying and fixing any issues that may arise. For example, we might use cookies to keep track of which website pages are most popular and which method of linking between website pages is most effective. The latter also helps us to track if you were referred to us by another website and improve our future advertising campaigns.
Another use of cookies is to store your log in sessions, meaning that when you log in to the members area to deposit funds, a "session cookie" is set so that the website remembers that you have already logged in. If the website did not set this cookie, you will be asked for your login and password on each new page as you progress through the funding process.
In addition, functional cookies, for example, are used to allow us to remember your preferences and identify you as a user, ensure your information is secure and operate more reliably and efficiently. For example, cookies save you the trouble of typing in your username every time you access our trading platform, and recall your preferences, such as which language you wish to see when you log in.
Here is an overview of some of the functions our cookies provide us with:
- Verifying your identity and detecting the country you are currently visiting from
- Checking browser type and device
- Tracking which site the user was referred from
- Allowing third parties to customize content accordingly
This website uses google analytics, a web analytics service provided by google, inc. ("google"). Google analytics uses analytical cookies placed on your computer, to help the website analyze a user's use of the website. The information generated by the cookie about your use of the website (including your IP address) may be transmitted to and stored by google on their servers. Google may use this information to evaluate your use of the website, to compile reports on website activity and to provide other services related to website activity and internet usage. Google may also transfer this information to third parties, where required to do so by law, or where such third parties process the information on behalf of google. Google will not associate your IP address with any other data held. By using this website, you give your consent to google to process data about you in the manner and for the purposes set out above.
Secure remote access and support
VNC® connect: the #1, fully encrypted VNC® software for cloud connectivity and direct access.
Stay safe during the covid-19 outbreak
Check out our home working resources to get set up fast
Secure, reliable screen sharing
Our products and services connect people and devices wherever they are, for control, support, administration, monitoring, training, collaboration and more. Save time and money, increase efficiency, reduce risk and create new business opportunities.

For IT pros, msps, enterprises and consumers
VNC® connect
Simple, secure, ready-to-use remote access and support software for all your computers and mobile devices.

For integrators, oems and iot
VNC® developer
Solutions and toolkits for integrating secure, real-time remote access into your own devices, products and services.
Trusted by world-class companies and IT professionals
Company
Products
Solutions for.
Get in touch
For feedback, sales or general enquiries, fill out our form, or call or chat with us during UK office hours.
Stay informed
Sign up for our newsletter, or follow us on social media.
Copyright © 2002- realvnc® limited. All rights reserved. Realvnc®, VNC® and RFB® are trademarks of realvnc® limited.
Nominal account
What is the nominal account?
Nominal accounts are accounts related and associated with losses, expenses, income, or gains. Examples include a purchase account, sales account, salary A/C, commission A/C, etc. The outcome of a nominal account is either profit or loss, which is then ultimately transferred to the capital account.
- The nominal account is an income statement account (expenses, income, loss, profit). It is also known as a temporary account, unlike the balance sheet account ( asset, liability, owner’s equity), which are permanent accounts.
- So nominal accounting starts with a zero balance at the start of every accounting year. Then during the period, it accumulates all the gains and losses and returns to zero balance at the end of every accounting year by transferring/paying the amount/ balances to a permanent account.

Nominal account example
Consider a temporary account like a sales account that is opened for recording the sale of goods and services during the year. At the end of the financial year, the total sales are transferred to the revenue statement account. Similarly, expenses are recorded in the expense account and which again at the end of the year are transferred to the revenue statement account. In the end, the positive/ negative changes (revenue- expenses) are transferred to a permanent account in the balance sheet.
Based on the periodicity of the flow of funds, the account is divided as below.
- An income is a short-term inflow of funds during the fiscal year.
- Expenses are the short-term outflow of the fund during the fiscal year.
- An asset is the long-term inflow of funds whose time horizon can be spread to multiple years, so assets value can be calculated as a present value of future cash flow.
- A liability is a long-term outflow of a fund that is extending beyond the financial year.

The rules of nominal account
The golden rules to record any transaction under nominal accounts are:
1.) debit all the expenses and losses.
2.) credit all the income and gains.
Let us understand the rules of nominal account with the help of an example:
Suppose a good is purchased for rs.15,000 in a cash transaction. To record this transaction, we are affecting two accounts i.E., purchase account and cash account.
The amount will be rs. 15,000 in both debit and credit.
Transferring fund from nominal account to real account
The following journal entries show how the balances in nominal ac are shifted through an income summary account to the retained earnings account-
#1 – shift all rs. 10,000 of revenues generated during the month to the income summary account
#2 – shift all rs. 9,000 of expenses generated during the month to the income summary account (there is assumed to be just one expense account)
#3 – shift the rs. 1,000 net profit balance in the income summary account to the retained earnings account
The preceding entries can be completed manually. However, an accounting software package will handle the transfer tasks automatically, once an authorized user sets the rollover flag in the software to close the old reporting year and shift recordkeeping to the next fiscal year.
Difference between a nominal account and a real account-
When we differentiate these two accounts, the main parameter we consider is the balances in these accounts at the end of the fiscal year.
- As we know, this account starts with zero balance and ends with zero balance, so only this account is called a temporary account. Whereas balance in a real account does not reset to zero at the end of fiscal year, and last year balances get to carry forward to the next fiscal year.
- These are income statement accounts i.E., accounts for recording income, expenses, profit, and losses. In contrast, a real account is linked with a balance sheet account i.E., accounts for recording assets, liabilities, owner’s equity.
- At the end of every fiscal year, the balances in nominal (temporary account) account are transferred to a real account (temporary account) for the net change during the accounting year. In other terms, the nominal account rule is reset to zero, and the balance is carry forwarded to a real account.
- Entries in the nominal account are recorded as per the journal entries concerning time and date.
Nominal account video
Recommended articles
This article has been a guide to what is nominal accounts. Here we discuss the golden rules to record any transaction with examples. Also, we discuss the nominal account vs. Real account. Here are the other articles in accounting that you may like –
Nominal account
What is the nominal account?
Nominal accounts are accounts related and associated with losses, expenses, income, or gains. Examples include a purchase account, sales account, salary A/C, commission A/C, etc. The outcome of a nominal account is either profit or loss, which is then ultimately transferred to the capital account.
- The nominal account is an income statement account (expenses, income, loss, profit). It is also known as a temporary account, unlike the balance sheet account ( asset, liability, owner’s equity), which are permanent accounts.
- So nominal accounting starts with a zero balance at the start of every accounting year. Then during the period, it accumulates all the gains and losses and returns to zero balance at the end of every accounting year by transferring/paying the amount/ balances to a permanent account.

Nominal account example
Consider a temporary account like a sales account that is opened for recording the sale of goods and services during the year. At the end of the financial year, the total sales are transferred to the revenue statement account. Similarly, expenses are recorded in the expense account and which again at the end of the year are transferred to the revenue statement account. In the end, the positive/ negative changes (revenue- expenses) are transferred to a permanent account in the balance sheet.
Based on the periodicity of the flow of funds, the account is divided as below.
- An income is a short-term inflow of funds during the fiscal year.
- Expenses are the short-term outflow of the fund during the fiscal year.
- An asset is the long-term inflow of funds whose time horizon can be spread to multiple years, so assets value can be calculated as a present value of future cash flow.
- A liability is a long-term outflow of a fund that is extending beyond the financial year.

The rules of nominal account
The golden rules to record any transaction under nominal accounts are:
1.) debit all the expenses and losses.
2.) credit all the income and gains.
Let us understand the rules of nominal account with the help of an example:
Suppose a good is purchased for rs.15,000 in a cash transaction. To record this transaction, we are affecting two accounts i.E., purchase account and cash account.
The amount will be rs. 15,000 in both debit and credit.
Transferring fund from nominal account to real account
The following journal entries show how the balances in nominal ac are shifted through an income summary account to the retained earnings account-
#1 – shift all rs. 10,000 of revenues generated during the month to the income summary account
#2 – shift all rs. 9,000 of expenses generated during the month to the income summary account (there is assumed to be just one expense account)
#3 – shift the rs. 1,000 net profit balance in the income summary account to the retained earnings account
The preceding entries can be completed manually. However, an accounting software package will handle the transfer tasks automatically, once an authorized user sets the rollover flag in the software to close the old reporting year and shift recordkeeping to the next fiscal year.
Difference between a nominal account and a real account-
When we differentiate these two accounts, the main parameter we consider is the balances in these accounts at the end of the fiscal year.
- As we know, this account starts with zero balance and ends with zero balance, so only this account is called a temporary account. Whereas balance in a real account does not reset to zero at the end of fiscal year, and last year balances get to carry forward to the next fiscal year.
- These are income statement accounts i.E., accounts for recording income, expenses, profit, and losses. In contrast, a real account is linked with a balance sheet account i.E., accounts for recording assets, liabilities, owner’s equity.
- At the end of every fiscal year, the balances in nominal (temporary account) account are transferred to a real account (temporary account) for the net change during the accounting year. In other terms, the nominal account rule is reset to zero, and the balance is carry forwarded to a real account.
- Entries in the nominal account are recorded as per the journal entries concerning time and date.
Nominal account video
Recommended articles
This article has been a guide to what is nominal accounts. Here we discuss the golden rules to record any transaction with examples. Also, we discuss the nominal account vs. Real account. Here are the other articles in accounting that you may like –
Temporary account in windows 10
I just downloaded windows 10. An 'upgrade' from 8.1. It won't let me access my files and whenever I log in it says it's giving me a temporary account and that the files I access won't be saved and what-not. Help?
Original title: just upgraded to windows 10
Thank you for posting in microsoft community. I understand your concern and I am glad to assist you.
This issue could arise because of user profile.
I would suggest you to log out from the current user profile and login with your microsoft account and check if the issue persist.
If the issue persists, I suggest you to follow the steps below and check if the issue is resolved.
Step 1: enable built-in administrator account.
Open elevated command prompt by entering safe mode with command prompt. T o go to safe mode, u se the power button on the sign-in screen and press shift + restart. This will take you to the recovery boot menu. Click troubleshoot> advanced options> startup settings. You then see a list where you can choose safe mode with command prompt.
Type the following command: net user administrator /active:yes
Login into the built in administrator user profile and create a new user profile with administrator privileges.
Delete the corrupted user account from the built in administrator.
Then lock your screen by pressing windows key + L, and sign-in at the administrator account.
Check if the issue persist and you can disable built in administrator account by typing the command: net user administrator /active:no in the command prompt (admin).
Step 2: to create a new user account follow the steps below:
Open elevated command prompt by right clicking on the start icon and select command prompt (admin).
Type net user newaccount password /add and click enter.
Type net localgroup administrators newaccount /add and click enter.
Log off from the system and login to the new user account.
You can also refer to the set up accounts on windows 10.
Hope this post helps. Get back to us for further queries. We are happy to help!
2 people found this reply helpful
Great! Thanks for your feedback.
How satisfied are you with this reply?
Thanks for your feedback, it helps us improve the site.
Secure remote access and support
VNC® connect: the #1, fully encrypted VNC® software for cloud connectivity and direct access.
Stay safe during the covid-19 outbreak
Check out our home working resources to get set up fast
Secure, reliable screen sharing
Our products and services connect people and devices wherever they are, for control, support, administration, monitoring, training, collaboration and more. Save time and money, increase efficiency, reduce risk and create new business opportunities.

For IT pros, msps, enterprises and consumers
VNC® connect
Simple, secure, ready-to-use remote access and support software for all your computers and mobile devices.

For integrators, oems and iot
VNC® developer
Solutions and toolkits for integrating secure, real-time remote access into your own devices, products and services.
Trusted by world-class companies and IT professionals
Company
Products
Solutions for.
Get in touch
For feedback, sales or general enquiries, fill out our form, or call or chat with us during UK office hours.
Stay informed
Sign up for our newsletter, or follow us on social media.
Copyright © 2002- realvnc® limited. All rights reserved. Realvnc®, VNC® and RFB® are trademarks of realvnc® limited.
So, let's see, what was the most valuable thing of this article: classification of elements, accounts, account heads into three types of accounts and the basis for classification. At real account 10
Contents of the article
- Free forex bonuses
- Account types or kinds of accounts - personal,...
- Personal accounts
- Tangible
- Nominal accounts
- Every account head belongs to one of the three...
- Accounting system - minimum accounting heads
- Assets and liabilities
- Assets a/c
- Liabilities a/c
- Incomes/gains and expenses/losses
- Expenses/losses a/c
- Incomes/gains a/c
- Minimum five account heads
- Elements effected by a transaction - identifying...
- The business is proposed to be started.
- Started business with a capital of 1,00,000.
- Bought furniture for cash 25,000
- Bought goods for cash 25,000 from M/s roxy...
- Bought goods from mr. Shyam rao on credit for...
- Sold goods for cash 20,000 to mr. Peter.
- Sold goods on credit to M/s bharat & co., for...
- Paid cash into bank 60,000.
- Paid cash to mr. Shyam rao, 5,000
- Received cash from M/s bharat & co., on account,...
- What is a real account?
- What does real account mean?
- Example
- Summary definition
- Enable the (hidden) administrator account on...
- Enable built-in administrator account in...
- Real account 10
- Secure remote access and support
- Secure, reliable screen sharing
- VNC® connect
- VNC® developer
- Trusted by world-class companies and IT...
- Company
- Products
- Solutions for.
- Get in touch
- Stay informed
- Nominal account
- What is the nominal account?
- Nominal account example
- The rules of nominal account
- Transferring fund from nominal account to real...
- Difference between a nominal account and a real...
- Nominal account video
- Recommended articles
- Nominal account
- What is the nominal account?
- Nominal account example
- The rules of nominal account
- Transferring fund from nominal account to real...
- Difference between a nominal account and a real...
- Nominal account video
- Recommended articles
- Temporary account in windows 10
- Secure remote access and support
- Secure, reliable screen sharing
- VNC® connect
- VNC® developer
- Trusted by world-class companies and IT...
- Company
- Products
- Solutions for.
- Get in touch
- Stay informed
No comments:
Post a Comment